Exercise and physical fitness have long been touted as essential components of a healthy lifestyle. They not only help maintain an ideal body weight but also improve overall physical health, mental well-being, and our ability to perform day-to-day activities with ease. In this blog, we’ll explore how regular exercise impacts our lives, the types of exercises that are most beneficial, and why incorporating fitness into your daily routine is crucial for both short-term and long-term health benefits.
Why Physical Fitness Matters
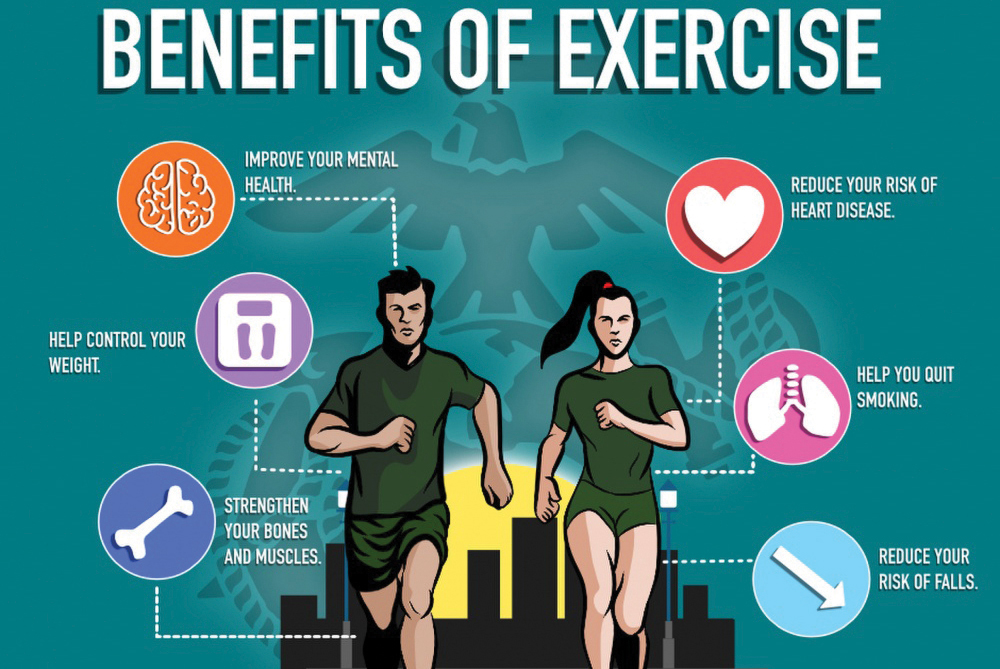
Physical fitness is more than just staying in shape or looking good. It encompasses the body’s ability to perform various physical tasks, endure prolonged periods of activity, and recover quickly from physical exertion. In today’s fast-paced world, where most people are glued to their desks or couches, the need for physical fitness is greater than ever.
Physical health benefits of exercise include:
- Improved cardiovascular health: Engaging in activities like running, swimming, and cycling strengthens the heart, reducing the risk of heart diseases.
- Weight management: Regular physical activity helps burn calories and regulate metabolism, reducing the risk of obesity.
- Enhanced muscle and bone strength: Weight-bearing exercises, such as strength training, increase muscle mass and improve bone density.
- Boosted immunity: Exercise stimulates the production of immune cells, which can help ward off illnesses and infections.
These are just a few examples of how exercise can directly impact your physical well-being.
Mental Health Benefits of Exercise

In addition to physical benefits, regular exercise can significantly improve mental health. Many studies have shown that exercise can be as effective as medication for treating mild to moderate depression and anxiety. Here’s how:
- Stress relief: Exercise triggers the release of endorphins, chemicals in the brain that act as natural painkillers and mood elevators. This leads to reduced stress and a more positive outlook on life.
- Enhanced cognitive function: Regular physical activity improves memory and learning. It increases blood flow to the brain, helping with concentration and mental clarity. Physical exercise has even been linked to preventing cognitive decline in older adults.
- Reduced anxiety: Exercise promotes relaxation and reduces levels of tension. Activities like yoga, swimming, and walking have been particularly effective in managing anxiety symptoms.
- Better sleep: Physical exertion during the day can help regulate sleep patterns, making it easier to fall asleep and stay asleep. Better sleep improves mood, productivity, and overall health.
Types of Exercise That Benefit Health

Not all exercises are the same. It’s important to include different types of activities that benefit various aspects of health and fitness.
- Aerobic exercises: These include activities like jogging, swimming, and cycling. Aerobic exercises improve cardiovascular endurance and are great for burning calories. They also help to reduce cholesterol levels and improve lung capacity.
- Strength training: Lifting weights or using resistance bands helps build muscle strength and improve bone density. This is particularly important for older adults, as it helps prevent osteoporosis and reduces the risk of falls.
- Flexibility exercises: Yoga, stretching, and Pilates increase flexibility, improving range of motion and reducing the risk of injury. Flexibility exercises also promote relaxation and stress relief.
- Balance exercises: Especially useful for older adults, balance exercises (like Tai Chi) can help prevent falls and improve stability.
Incorporating all of these exercise types into your routine creates a well-rounded fitness plan that addresses cardiovascular health, strength, flexibility, and balance.
How Physical Fitness Affects Daily Activities

Our daily lives demand a lot from our bodies. Whether it’s lifting heavy objects, walking long distances, or staying focused at work, physical fitness plays a pivotal role in how well we manage these tasks.
- Increased energy levels: When you engage in regular physical activity, your cardiovascular system works more efficiently, delivering oxygen and nutrients to your tissues. This helps you feel more energized throughout the day, making daily tasks less tiring.
- Improved productivity: A study published by the Harvard Business Review found that employees who exercise regularly are more productive, have better focus, and take fewer sick days than their sedentary peers. Exercise promotes mental clarity, allowing you to concentrate on tasks for longer periods of time.
- Better posture and reduced back pain: Many people suffer from back pain due to poor posture and weak core muscles. Incorporating strength training and flexibility exercises into your routine can alleviate this pain and improve your posture, making sitting, standing, and walking more comfortable.
- Better coordination and balance: Activities that improve balance and flexibility, such as yoga or Pilates, can enhance your body’s coordination, helping you move with more ease and preventing accidents like slips and falls.
- Faster recovery from physical tasks: Have you ever noticed how after a long period of inactivity, even light tasks can feel overwhelming? Regular physical fitness keeps your body in a state of readiness, enabling quicker recovery after physical activity.
Exercise and Long-Term Health Benefits

Regular physical activity also has long-term health benefits that can improve the quality of life as you age:
- Reduced risk of chronic diseases: Regular exercise lowers the risk of developing chronic conditions such as heart disease, Type 2 diabetes, and certain cancers.
- Improved longevity: Studies show that people who engage in regular physical activity live longer than those who do not. This is because exercise helps maintain a healthy heart, strong muscles, and a balanced metabolism, all of which are key factors in longevity.
- Preventing cognitive decline: According to research from the Alzheimer’s Association, regular exercise may protect against Alzheimer’s disease and other forms of dementia by maintaining blood flow to the brain and supporting brain cell growth.
Incorporating Exercise Into Your Routine
Now that you know how exercise and physical fitness influence health and daily life, the next step is to find ways to incorporate fitness into your routine. Here are some practical tips:
- Start small: If you’re new to exercise, start with small, manageable goals. A 10-minute walk after dinner or a few stretches in the morning can make a big difference.
- Make it enjoyable: Find an activity you enjoy, whether it’s dancing, cycling, or swimming. The more you enjoy your workout, the more likely you are to stick with it.
- Stay consistent: Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week. Consistency is key to reaping the full benefits of physical fitness.
- Mix it up: Incorporate a mix of aerobic, strength, flexibility, and balance exercises to keep your workout interesting and target different areas of fitness.
- Get a workout buddy: Exercising with a friend can make fitness more enjoyable and provide accountability.
Final Thoughts: Exercise Is Key to a Healthy Life
Exercise and physical fitness have profound effects on our health and day-to-day activities. From reducing the risk of chronic diseases to improving mental health, physical activity enhances every aspect of life. Incorporating a well-rounded fitness routine that includes aerobic, strength, flexibility, and balance exercises will not only improve your physical and mental well-being but also help you perform daily tasks with more energy and ease.
For more information on fitness routines and tips on staying active, check out WebMD’s Guide to Physical Fitness. Additionally, the Mayo Clinic’s Exercise for a Healthy Lifestyle provides excellent resources on building healthy habits through exercise.
Take the first step towards better health by incorporating exercise into your daily routine, and you’ll soon see the benefits in every aspect of your life!